In industrial projects, navigating risks is critical to ensuring budget accuracy and project success. Integrating risk analysis into project estimating provides a structured approach to identify, quantify, and address uncertainties that can impact costs and schedules. By proactively incorporating risk management into estimates, project teams can make informed decisions, reduce the likelihood of cost overruns, and build resilience against unforeseen challenges.
This article explores actionable strategies and tools for incorporating risk analysis into project estimating, helping teams transform uncertainty into opportunity.
Why Integrate Risk Analysis into Project Estimating?
Risk is an inherent part of any project, particularly in large-scale industrial endeavors where the stakes are high. Estimating without considering risk leaves projects vulnerable to cost overruns, schedule delays, and resource shortages. Integrating risk analysis into estimating provides the following benefits:
- Improved Accuracy: Identifying and quantifying risks helps refine cost and schedule estimates.
- Enhanced Decision-Making: Risk-informed estimates enable project managers to make better financial and strategic decisions.
- Proactive Planning: Risk analysis highlights potential challenges, allowing teams to mitigate them before they arise.
- Stakeholder Confidence: A transparent approach to risk management fosters trust among stakeholders.
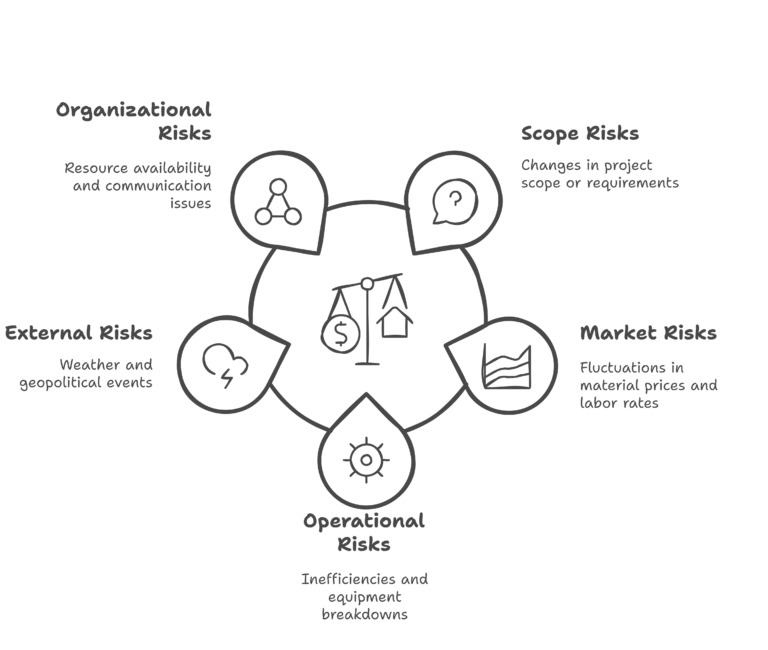
Types of Risks in Project Estimating
Before integrating risk analysis, it’s essential to understand the types of risks that can affect project estimates:
- Scope Risks
Changes in project scope, design modifications, or poorly defined requirements can lead to cost increases and schedule extensions.
- Market Risks
Fluctuations in material prices, labor rates, or currency exchange rates impact cost estimates.
- Operational Risks
Inefficiencies, equipment breakdowns, and unforeseen technical challenges can disrupt project execution and inflate costs.
- External Risks
Weather conditions, regulatory changes, and geopolitical events can cause delays or necessitate additional expenses.
- Organizational Risks
Resource availability, management expertise, and communication breakdowns within the project team can influence estimates.
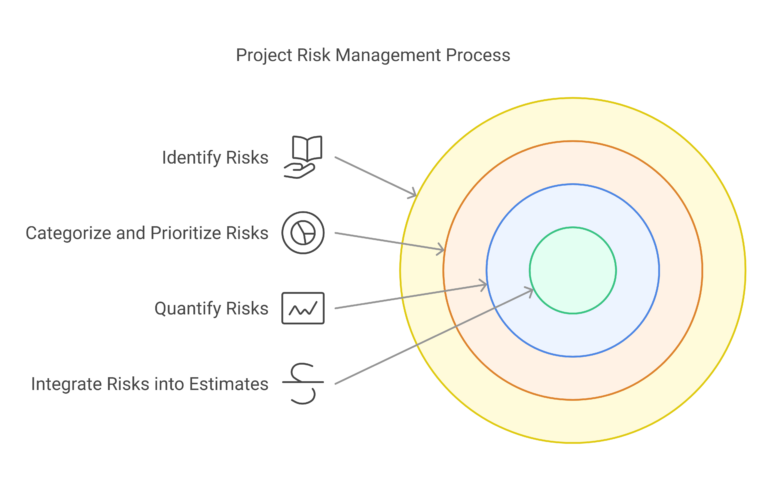
Steps to Integrate Risk Analysis into Project Estimating
Identify Risks
The first step in integrating risk analysis is identifying potential risks that could affect project costs and schedules. This involves collaboration across stakeholders, including engineers, contractors, and project managers.
Methods for Risk Identification:
- Brainstorming Sessions: Gather input from project teams to identify potential risks.
- Historical Data Review: Analyze data from similar past projects to identify recurring risks.
- Checklists: Use industry-standard risk checklists as a starting point.
Categorize and Prioritize Risks
Once risks are identified, categorize them by type (e.g., scope, market, operational) and prioritize them based on their potential impact and likelihood.
Prioritization Techniques:
- Risk Matrix: Plot risks on a matrix based on their likelihood (low, medium, high) and impact (low, medium, high).
- Risk Ranking: Assign numerical scores to risks and rank them accordingly.
Quantify Risks
Quantifying risks involves estimating their potential impact on costs and schedules. This step requires detailed analysis and often includes statistical methods.
Quantification Techniques:
- Three-Point Estimating: For each risk, calculate an optimistic, pessimistic, and most likely estimate to determine a range of potential impacts.
- Monte Carlo Simulation: Use probabilistic modeling to simulate multiple project scenarios and identify the range of possible outcomes.
- Contingency Allocation: Assign contingency funds to account for risks, based on their likelihood and impact.
Integrate Risks into the Estimate
Incorporate identified and quantified risks into the overall project estimate. This process involves adjusting both cost and schedule baselines to reflect potential uncertainties.
Methods of Integration:
- Cost Buffers: Add contingency funds to specific line items or the overall budget to address identified risks.
- Schedule Buffers: Include time buffers in the project timeline to accommodate potential delays.
- Scenario Planning: Develop multiple estimate scenarios (e.g., best-case, worst-case, and most likely) to account for uncertainties.
How Risks Are Added to Estimates: Risks are typically incorporated into project estimates in one or more of the following ways:
- Line-Item Adjustments: Individual cost items or work packages include risk-based contingencies directly tied to specific identified risks (e.g., higher material costs due to market volatility).
- Overall Contingency Reserves: A percentage of the total project budget is allocated as a general contingency to address unforeseen risks that are not specifically quantified.
- Schedule Contingencies: Buffer periods are added to the project schedule to manage risks associated with delays, such as regulatory approvals or weather impacts.
- Cost Escalation Factors: Multipliers are applied to adjust for inflation or other market trends linked to identified risks.
Monitor and Update Risk Analysis
Risk analysis is not a one-time exercise; it must be continuously monitored and updated as the project progresses and new information becomes available.
Monitoring Practices:
- Risk Reviews: Schedule regular risk review meetings to assess emerging risks and update existing ones.
- Variance Analysis: Compare actual project costs and schedules to the estimated baselines to identify discrepancies caused by risks.
- Lessons Learned: Document the impact of risks and their mitigation strategies to improve future estimates.
Tools and Techniques for Risk-Based Estimating
Monte Carlo Simulation
Monte Carlo simulation is a powerful tool for integrating risk analysis into project estimating. It uses statistical models to simulate thousands of potential project outcomes, providing a probability distribution for costs and schedules.
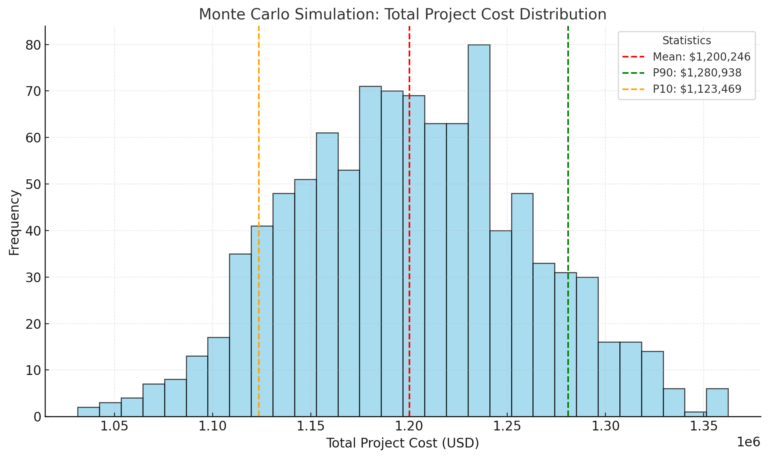
Advantages:
- Offers a range of possible outcomes instead of a single-point estimate.
- Identifies high-probability risks and their impacts.
Sensitivity Analysis
Sensitivity analysis examines how changes in key variables (e.g., material costs, labor rates) affect the overall estimate. This helps identify the most influential risks.
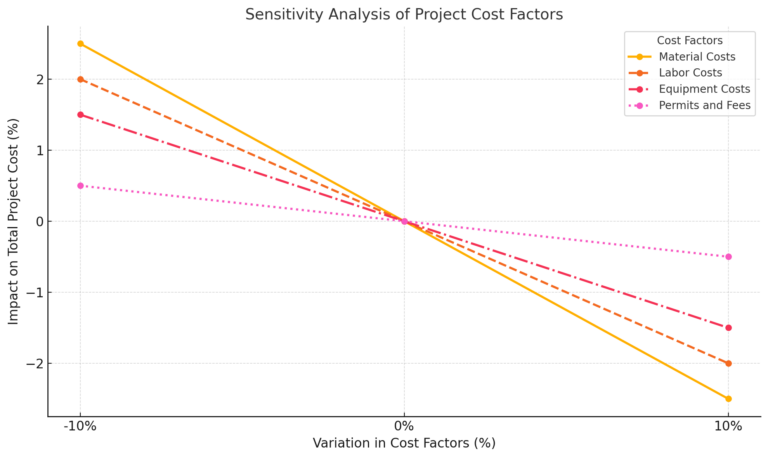
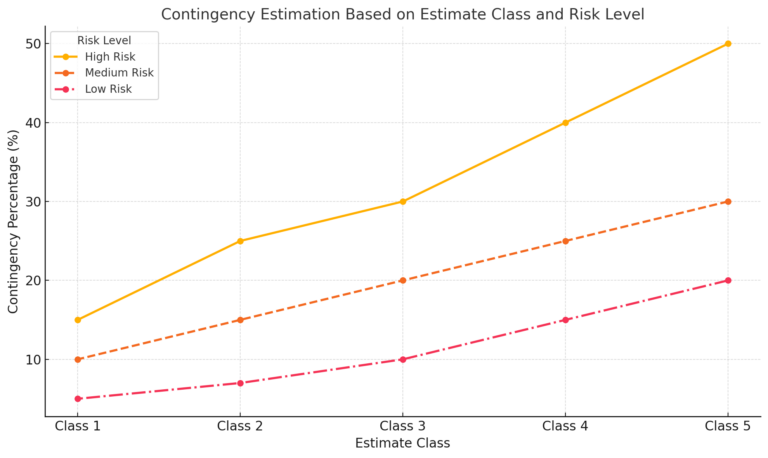
Contingency Estimating
Contingency estimating involves allocating funds or time buffers specifically for risk-related uncertainties. These contingencies can be adjusted as risks are better understood.
Risk Registers
A risk register is a centralized document that tracks identified risks, their likelihood, impact, mitigation plans, and status. It serves as a valuable reference throughout the project lifecycle.
| Risk ID | Risk Description | Category | Likelihood | Impact | Risk Level | Mitigation Strategy | Owner | Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R-001 | Delay in material delivery | Supply Chain | High | High | Critical | Establish alternative suppliers and expedite orders | Procurement Team | Open |
| R-002 | Safety incident during construction | Health & Safety | Medium | High | High | Conduct safety training and enforce PPE compliance | Safety Officer | Open |
| R-003 | Regulatory approval delays | Regulatory | Low | High | Medium | Engage with regulators early and ensure compliance | Compliance Lead | In Progress |
| R-004 | Labor shortage | Workforce | Medium | Medium | Medium | Secure subcontractor agreements and adjust schedules | HR Manager | Open |
| R-005 | Equipment failure during operations | Equipment | Low | Medium | Low | Perform pre-operation equipment inspections | Maintenance Team | Open |
| R-006 | Cost overrun due to design changes | Financial | Medium | High | High | Freeze design early and implement strict change control | PMO | Open |
| R-007 | Adverse weather impacting schedule | Environmental | High | Medium | High | Develop contingency schedule and monitor forecasts | Construction Manager | Open |
| R-008 | Cyberattack on control systems | IT | Low | High | Medium | Implement robust cybersecurity measures | IT Security Team | Open |
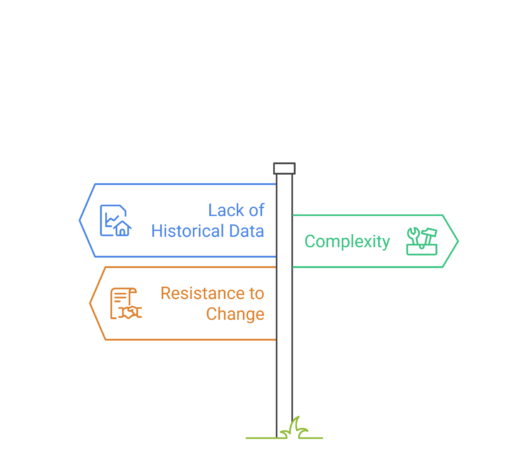
Challenges in Risk-Based Estimating
Lack of Historical Data
Without reliable historical data, it can be challenging to quantify risks accurately.
Complexity
Risk analysis methods like Monte Carlo simulation require expertise and computational tools, which may not be available in all organizations.
Resistance to Change
Some stakeholders may resist integrating risk analysis, viewing it as an unnecessary complication or cost.
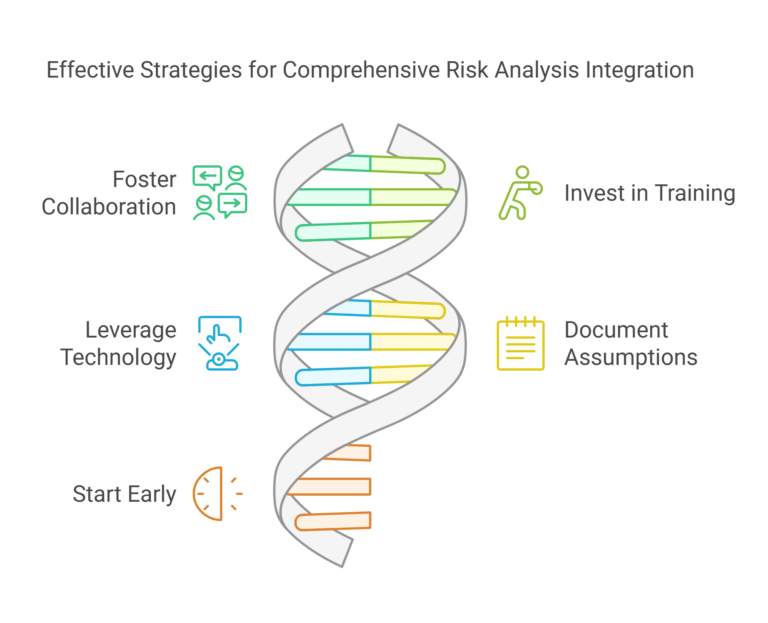
Best Practices for Integrating Risk Analysis
- Foster Collaboration
Involve stakeholders from all disciplines in risk identification and quantification to ensure comprehensive coverage.
- Invest in Training
Equip project teams with the skills and knowledge to apply risk analysis methods effectively.
- Leverage Technology
Adopt modern software tools for risk analysis and simulation, such as Primavera Risk Analysis or @Risk.
- Document Assumptions
Clearly document all assumptions used in risk analysis to ensure transparency and facilitate future reviews.
- Start Early
Incorporate risk analysis into estimating as early as possible to guide decision-making during project planning.
Real-World Example: Integrating Risk Analysis
Imagine an oil and gas pipeline project estimated at $500 million. Using risk-based estimating:
- Identified Risks: Potential risks include labor shortages, material price fluctuations, and regulatory delays.
- Quantified Risks: Monte Carlo simulation reveals a 30% chance that material costs will exceed the baseline by 15%.
- Integrated Risks: A $10 million contingency is added for material cost overruns, and a 4-week schedule buffer is included to account for regulatory delays.
- Ongoing Monitoring: Regular risk reviews track market trends and adjust contingencies as needed.

Conclusion
Integrating risk analysis into project estimating transforms estimates from static numbers into dynamic tools that reflect the realities of energy projects. By accounting for uncertainties and proactively addressing potential challenges, project teams can develop more accurate budgets, reduce the likelihood of cost overruns, and enhance stakeholder confidence.
While implementing risk-based estimating requires effort and expertise, the benefits far outweigh the costs. With the right tools, processes, and mindset, organizations can embrace risk as a manageable variable, turning it into an asset rather than a liability. In the high-stakes world of energy projects, this approach is not just advantageous—it’s essential.
Disclaimer
The information provided in this post is for reference purposes only and is intended to serve as a guide to highlight key topics, considerations, and best practices. It does not constitute professional advice or a substitute for consulting regarding specific projects or circumstances. Readers are encouraged to evaluate their unique project needs and seek tailored advice where necessary. Please Contact Us to discuss your particular project.







